P37.104: Substation Corrosion Management
Objective
All assets within a substation are subject to degradation and have maintenance programs to extend the service life or a replacement scheduled. This project provides guidance in understanding the degradation rates of assets in soil and atmospheric exposure, how to select the appropriate corrective action, and how to ensure that the corrective action is aligned with the environment.
Ground grid integrity is a critical factor governing the safety and reliability of a substation or switchyard. Copper is the typical material used in the construction of a ground grid because of its corrosion resistance in most soil series. Degradation of the grid, however, can still occur when this material is present. A few possible reasons are application outside the design specifications, chemically incompatible soils, or the presence of stray current. These tasks help understand what existing tools or techniques can identify locations within the ground grid that do not meet the design specifications and represent risk to the utility.
The objective of this project is to understand how substation assets degrade in soil and atmospheric exposure and where this represents risk to the utility. This is achieved through:
- Evaluating existing, new, and emerging inspection technologies to understand the limitations and benefits so that utilities can select these tools based on the construction specifications
- Determining corrosivity levels of the soil series at a substation so that engineers can select the appropriate materials for the ground grid designs, foundations, and tank bottoms
- Determining corrosivity levels of the soil series at a substation so that maintenance personnel understand when to inspect and maintain the ground grid and other substation assets
- Defining corrosion control options and providing guidance for the appropriate mitigation methods for substation assets in soil exposure
Research Value
This research can provide the following value:
- Provide guidance to asset management teams for life-cycle decisions
- Develop processes and training for inspection and maintenance operations
- Optimize maintenance budgets through population assessment (targeted inspections) and predictive maintenance of ground grids
- Develop guidelines for material selection and application to reduce theft of grounding system conductors and optimize corrosion control
- Help understand and manage risks through prioritized inspections
- Improve worker and public safety by proactively identifying areas of ground grid degradation
- Assess the potential of a cathodic protection system to detect ground grid theft
Planned 2025 Research
Each research task in 2025 is designed to provide value to the funding utility, and each task has a different level of complexity. Some tasks may require more time to mature, and, in some instances, the results are incorporated into future work. Therefore, the research approach for understanding corrosion on substation assets is categorized by short-, medium-, and long-term research for the reader to understand its value.
Short-Term Research:

Refinement of Impressed Current Cathodic Protection for Corrosion Control on Ground Grids: Cathodic protection (CP) is one of the primary corrosion control methods for managing degradation of ground grids because of soil exposure. When applied properly, CP may also offset the effects of stray and circulating currents because of connectivity to the transmission lines and operation of the substation equipment. A temporary CP system was installed at EPRI’s Lenox, Massachusetts laboratory in 2020, and the resulting voltage gradients were plotted to show locations where the protection was insufficient and discharge locations remained.
In 2021 and 2022, the process was refined by adding new equipment to level the potentials throughout the Lenox substation and eliminate discharge locations. The findings are that CP systems must be carefully designed to eliminate additional circulating currents. In 2025, research will focus on the development of a web app supporting cathodic protection design, installation, and maintenance operations.
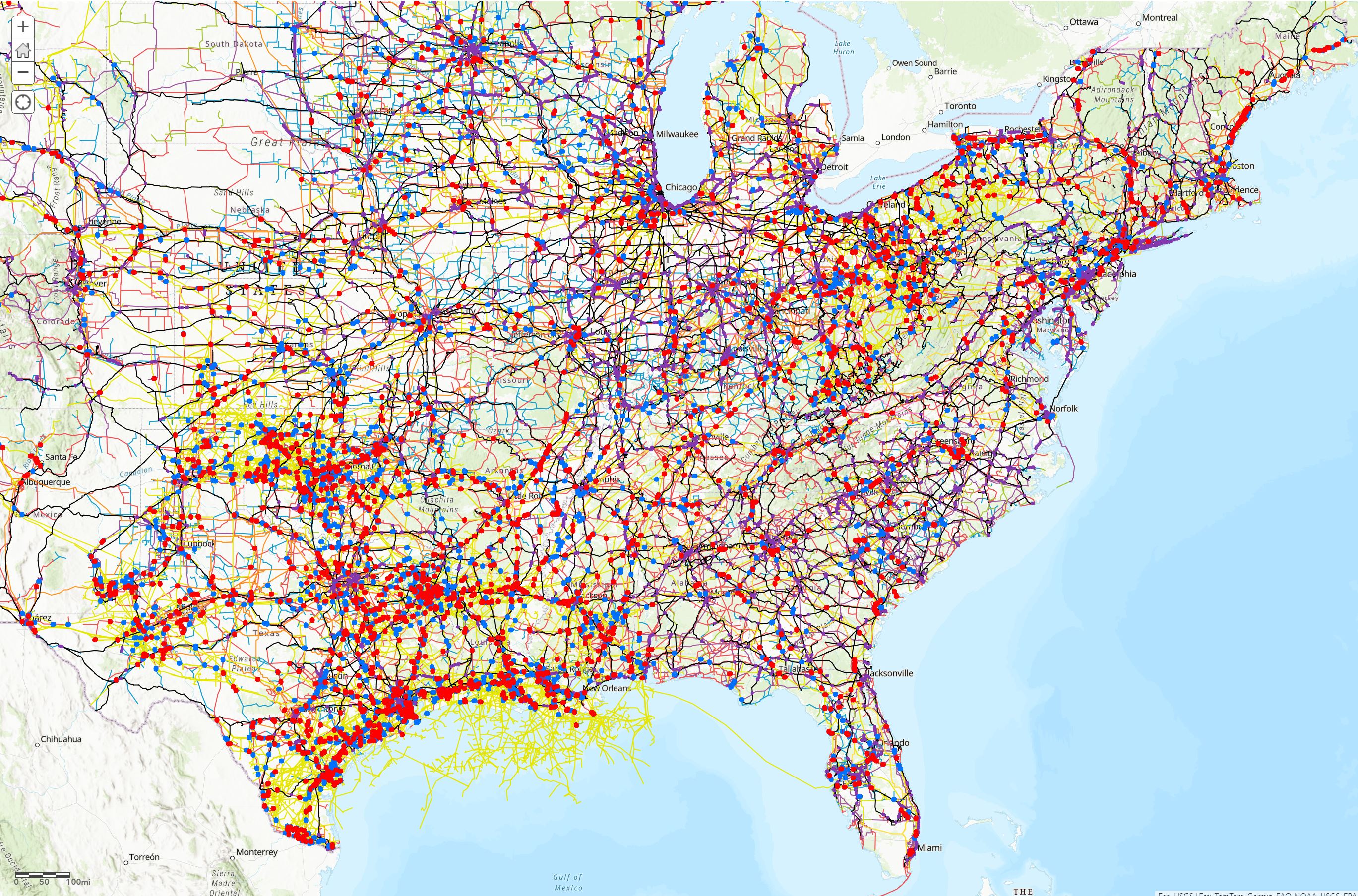
Corrosion Due to AC and DC Stray and Circulating Currents: The effects and severity of alternating current (ac) corrosion coupled with direct current (dc) stray currents have been studied and quantified in previous research. This task explores the methods to screen and quantify the effects as well as the mitigation options for these corrosion-related issues. Mapping circulating currents allows engineers to understand where problematic locations exist within the substation. This makes the design of a corrosion control system much more effective and cost-efficient.
Research in 2025 will continue to focus on modeling induced voltages and resulting stray circulating currents. This is anticipated to augment the existing metrics for the GIS models that have been developed and are being validated.

Field Guides: A field guide is a pocket reference book that allows personnel to identify, quantify, and prescribe a corrective action based on illustrations depicting levels of corrosion severity.
Medium-Term Research:
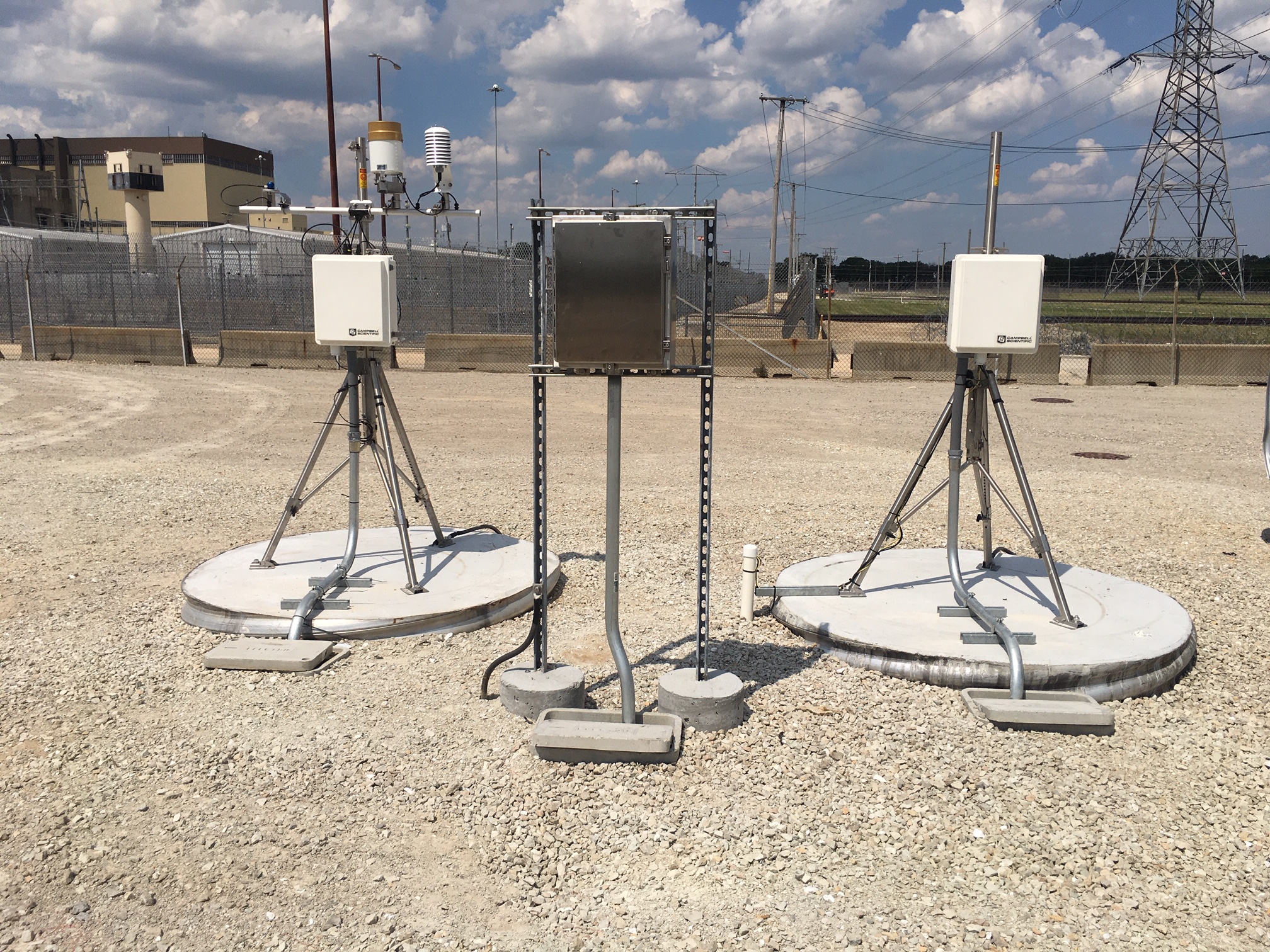

Sensor Development to Discriminate Between Localized, General, and Stray Current Corrosion: Corrosion depends on environmental factors, such as moisture, temperature, pH, and stray or circulating currents. To understand and delineate between the many types of corrosion, EPRI has developed a sensor array that helps researchers and asset managers identify and quantify the severity of each type of corrosion. The array’s capabilities were expanded in past years to measure atmospheric weather patterns to correlate those factors with changes in subgrade corrosion. Ongoing research is focused on analyzing large data sets from these individual sensors in the array to further our understanding of diurnal changes in corrosion activity for substation assets exposed to soil.
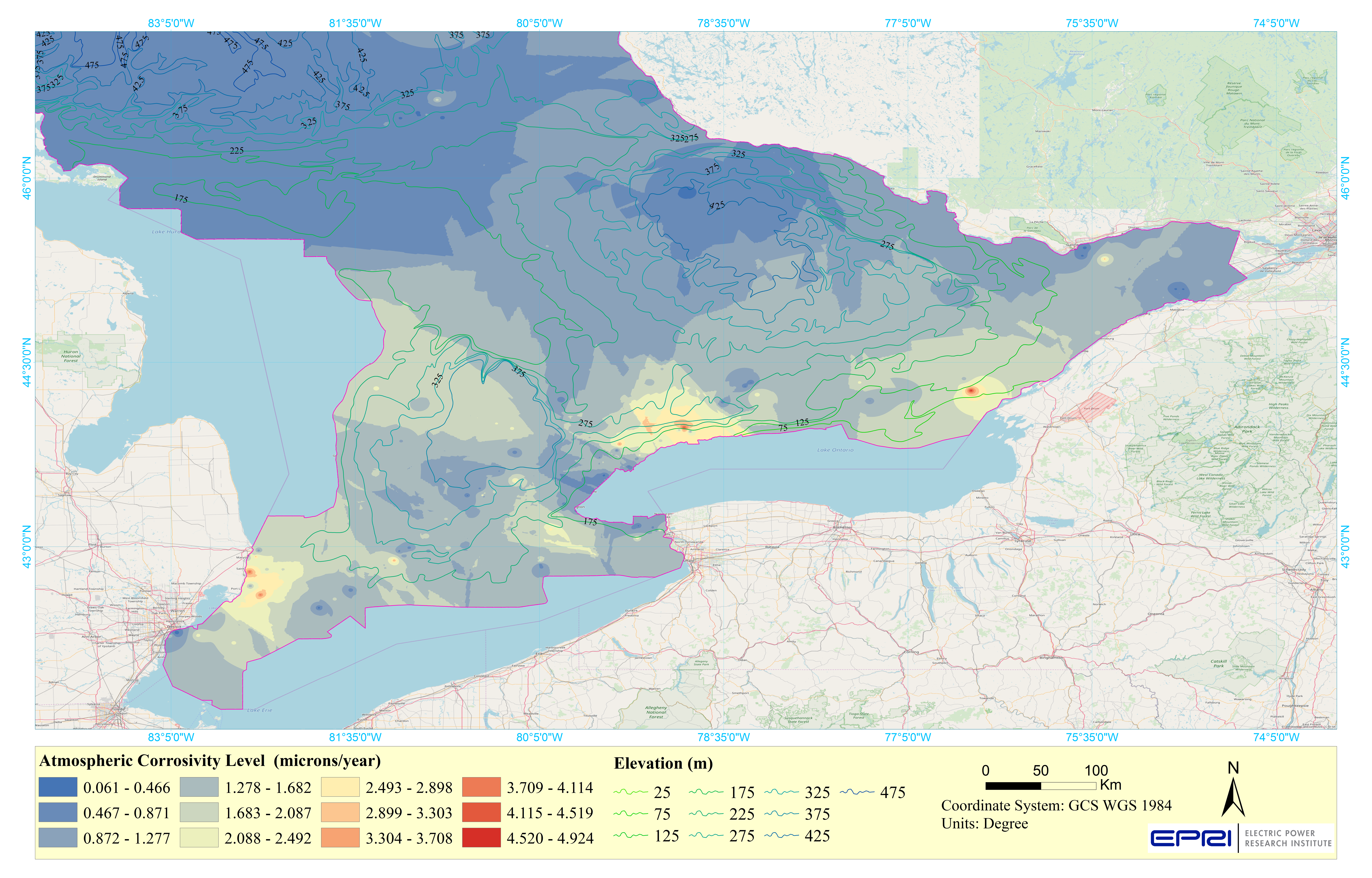
Atmospheric Corrosivity Maps: Atmospheric Corrosion in Substations: Environments can vary within a substation because of energized equipment, proximity to a generation plant, and topography at the site. This makes forecasting for maintenance operations because of atmospheric corrosion within a substation a challenge. Having corrosion rates for steel, zinc, and aluminum within a substation allows asset managers to understand and forecast for maintenance and replacements.
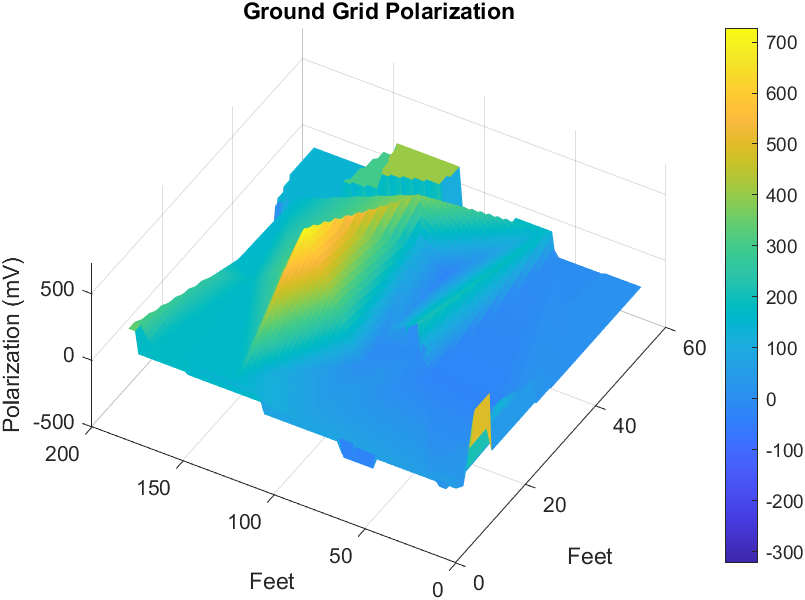
Atmospheric Corrosivity Maps: Voltage Gradient Mapping: Corrosion severity may be understood by measuring the potential of a metal in soil exposure. This is useful when reviewing a copper grounding system to determine if the grid is picking up or discharging corrosion current. Creating a voltage gradient map allows visualization of the equipotential lines within a substation and refinement of the locations requiring further investigation.
Long=Term Research:

Evaluation of Ground Grid Inspection Technologies: Four inspection technologies for ground grids have been evaluated at EPRI’s 138-kV substation. Each tool has performance metrics evaluated and will be deployed at a utility’s service territory to evaluate operational limits and performance in the field. The goal is to understand the benefits and limitations for each technology, which will allow a utility to select the technique or technology that is appropriate for their specifications. Additional inspection technologies will be identified and evaluated, and the results will be published for inclusion along with the three-tiered inspection process in the Ground Grid Corrosion Management Guidelines.
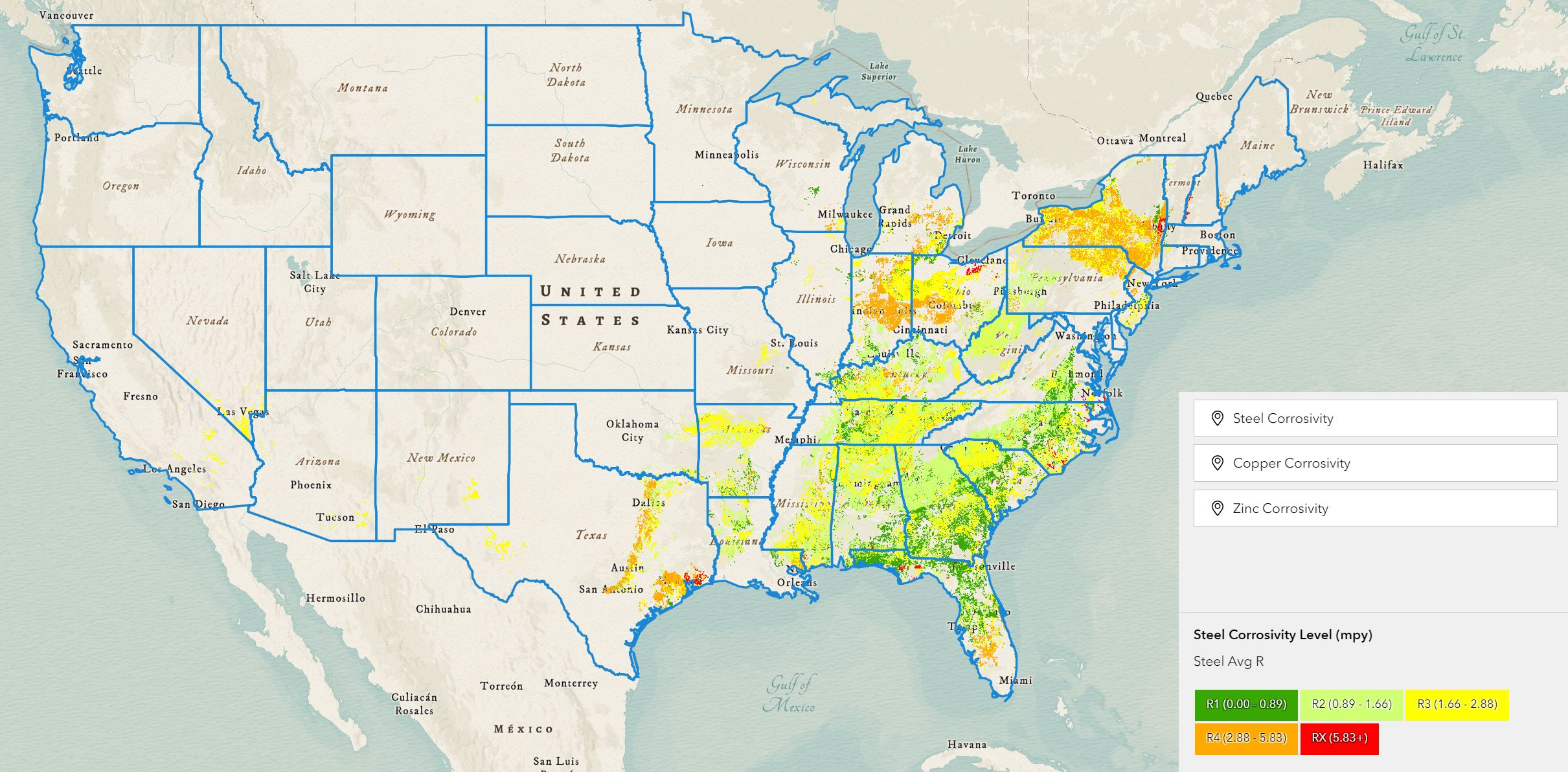
Subgrade Corrosion on Ground Grids: This task is an overview of all the new learning in the form of guidelines for ground grid corrosion. This includes inspection, assessment, and mitigation techniques and technologies that may be studied and implemented by utility personnel.

Subgrade Corrosion in Substations: Corrosion is not limited to ground grids but is also seen in tank bottoms, foundations, underground piping, and communications assets. The objective of this task is to develop a suite of inspection tools or technologies and best-in-class methods to mitigate or arrest corrosion on these assets.
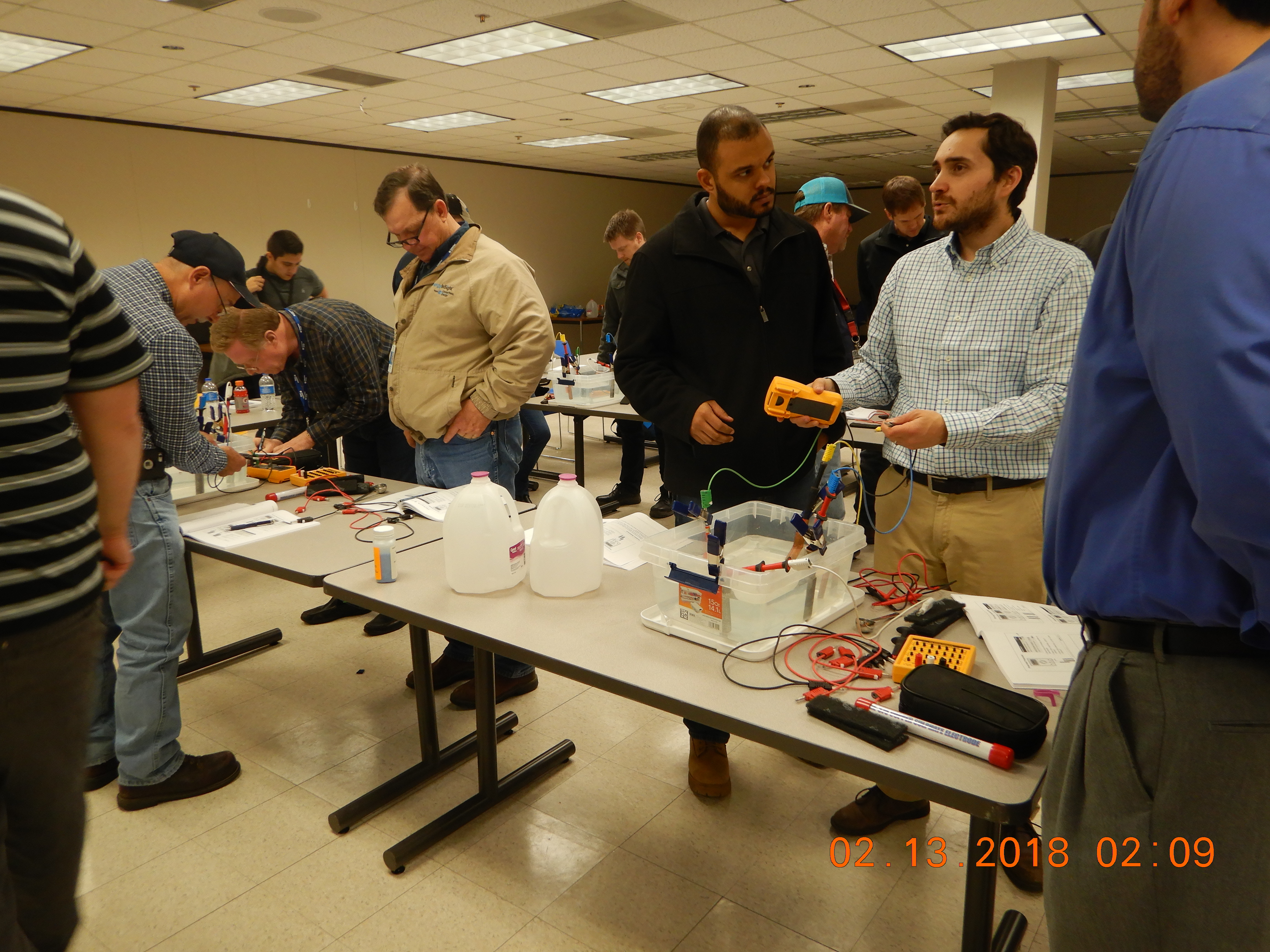

Corrosion and Corrosion Control Workshop: Held every two years, this workshop provides both theory and practical experience in understanding corrosion and how to assess and implement various types of corrosion control technologies. The workshop is designed to support asset managers, engineers, maintenance managers, and field crews in gaining practical knowledge for extending the service life of their assets.

Corrosion Management Guidebook: Guidance on corrosion management is needed for all areas of power delivery. This guidebook contains asset management information for inspection, assessment, mitigation, and remediation for all departments within a utility. The guidebook contains the fundamentals of corrosion, guidance for inspection and assessment, and an understanding of mitigation methods that align with the environment.
Anticipated Deliverables
| Deliverable | Date |
|---|---|
| Stray and Circulating Current Corrosion Control | December 31, 2025 |
| Atmospheric Corrosion in Substations | December 31, 2025 |
| Monitoring Ground Grid Performance at Corrosion Discharge Locations | December 31, 2025 |
| Identifying Corrosion Locations Through Equipotential Line Mapping | December 31, 2025 |
| Corrosion Management Reference Book | December 31, 2025 |
Past EPRI Research on Topic
| Product ID | Title | Description | Published Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3002021374 | Ground Grid Protection Methods: Cathodic Protection Changes with Increased Impedance | Refines the efficacy of a cathodic protection system as segments of a ground grid are removed from operation. | December 2021 |
| 3002024603 | Evaluation of Ground Grid Inspection Technologies | This deliverable continues the evaluation of new and emerging inspection technologies but also begins development of a training module for early career engineers, technicians, and field crews. | December 2022 |
| 3002027081 | Workshop for Corrosion Fundamentals and Corrosion Control | This course is designed to support all departments within transmission and distribution and allow an understanding of how to extend the service life of their assets. | December 2023 |
| TBD | Field Guide: IAM of Substation Ground Grids | Substation Ground Grid Inspection and Assessment Field Guide. | December 2024 |