Objective
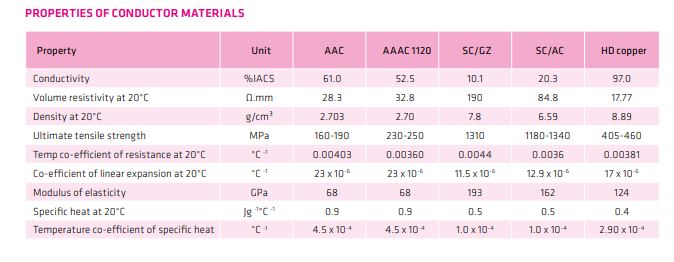
The overhead transmission system is facing a challenging time with an aging infrastructure and increased power demands. To ensure safe, reliable, and efficient power transmission, it is important that we make the best decisions when selecting, specifying, installing, and maintaining overhead transmission conductors and connectors. This project focuses on performing research to provide effective guidance for member utilities to select, specify, install, and maintain traditional conductors and connectors. Traditional conductors and their connectors include copper (Cu) conductors, all-aluminum conductors (AAC), aluminum conductor alloy-reinforced (ACAR) conductors, all-aluminum alloy conductors (AAAC), and aluminum conductor steel-reinforced (ACSR) conductors.
The objectives of this project focus on reducing operational and maintenance costs, improving reliability, and ensuring safety of utility workers and the general public by improving the processes of selecting, installing, inspecting, and maintaining traditional conductors and connectors. EPRI’s research objectives include:
- Understanding the performance and degradation mechanisms of traditional conductors and connectors through laboratory testing and assessments of components from the field
- Assessing the performance of existing traditional conductor and connector inspection technologies
- Developing guidelines for inspection and acceptance criteria for traditional conductors and connectors
- Identifying and evaluating new and emerging inspection technologies
- Evaluating the efficacy of mitigation strategies for degraded conductors and connectors
Research Value
Selecting, installing, inspecting, and maintaining overhead transmission conductors efficiently and effectively reduces operational and maintenance costs, improves reliability, and ensures safety of utility workers and the public. By performing research on traditional conductors and connectors, this project aims to:
- Improve reliability by selecting the appropriate conductor and connectors
- Reduce sustained, unplanned outages due to conductor and connector failure
- Improve reliability by providing guidance on prioritizing inspections
- Improve reliability and operational and maintenance costs by providing guidance on inspection methodologies and techniques
- Improve reliability by providing clear acceptance criteria for conductors and connectors
- Improve productivity of field personnel and address loss of experienced personnel with training and field tools
Approach
EPRI intends to improve reliabiltiy, safety, and efficiency by performing the following tasks in 2026:

Identify Methods for In-Service Conductor Identification: In 2026, new and emerging conductor and connector inspection technologies are expected to be identified, reviewed, and evaluated. Some utilities struggle to identify conductors that have been on their system for decades. EPRI intends on evaluating methods and tools to identify in-service conductors and update the Traditional Conductor and Connector Inspection Guide with their findings.
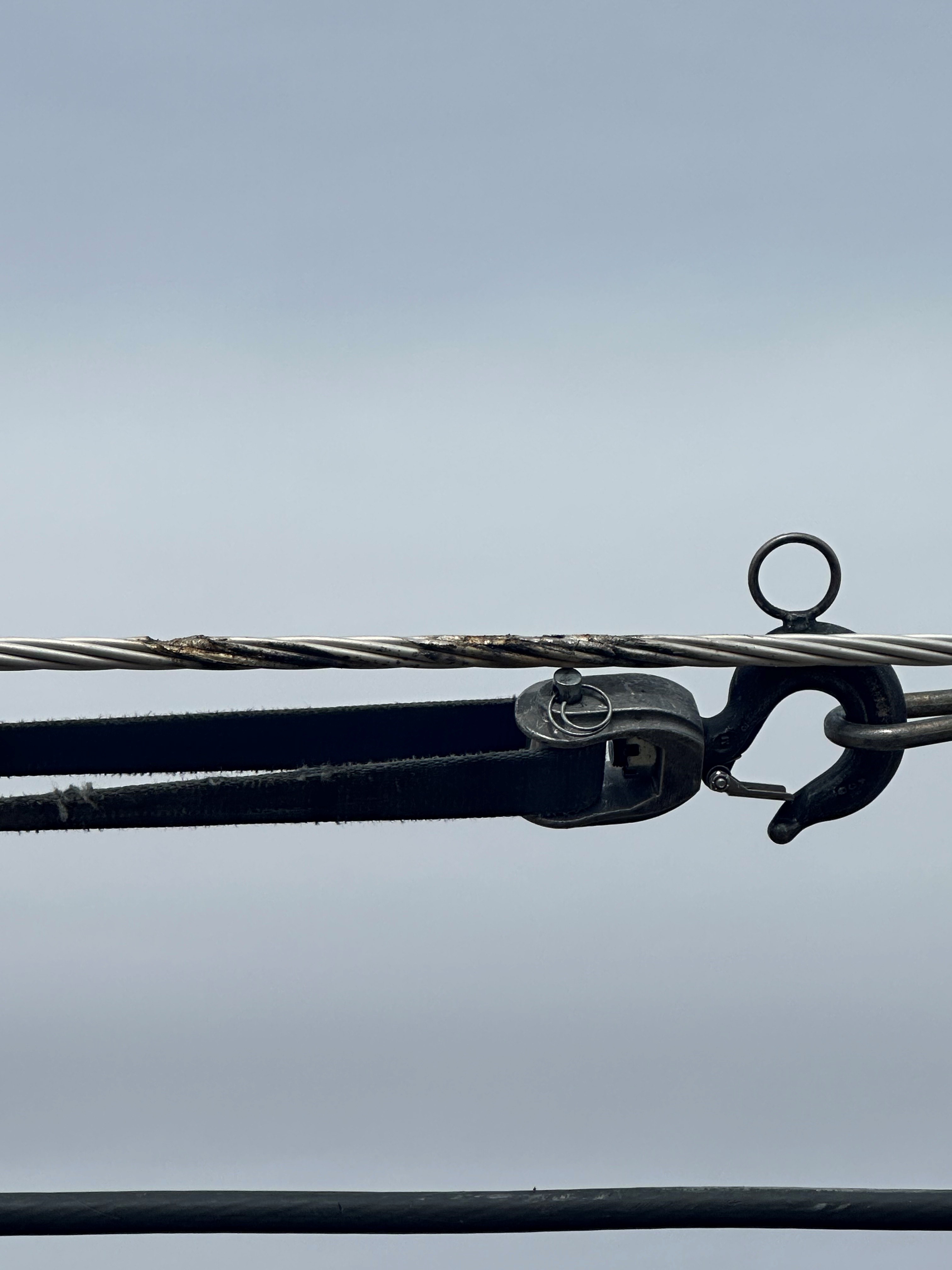

Analyze Failed or Removed-from-Service Conductors and Connectors: Conductors and connectors that have failed in service or have been removed from service are evaluated in the laboratory to better understand aging and failure modes. Tests may include resistance measurements, thermal responses, infrared (IR) measurements, radiographic analysis, and dissection or mechanical tensile testing to failure. EPRI aims to include and track this information in a database to identify trends in the industry. In 2026, EPRI plans to continue evaluating aged and failed samples and update to the report Evaluation of Aged Traditional Conductors and Connectors.

Continue Accelerated Aging of Single-Stage Compression Fittings at 93°C: EPRI has provided guidelines to assist utilities with the inspection and management of line connectors based on previous EPRI empirical testing of traditional conductors and connectors. Recently, manufacturers have developed new single-stage compression connector designs for traditional conductors, however, their long-term performance is unknown. In 2026, EPRI intends to continue the accelerated aging of newly developed single-stage compression fittings for traditional conductors at 93°C to understand their performance and degradation mechanisms over a simulated 40-year lifespan.

Provide Guidance on Inspection and Assessment of T-Tap Connectors: Guidelines help to assist utilities with managing connectors through their lifetime, including scheduling of inspections, selection inspection methods, data collection and use, prioritizing, and mitigation strategies. In 2026, EPRI intends on detailing inspection methods and acceptance criteria for T-tap connectors in the Traditional Conductor and Connector Management Guide.
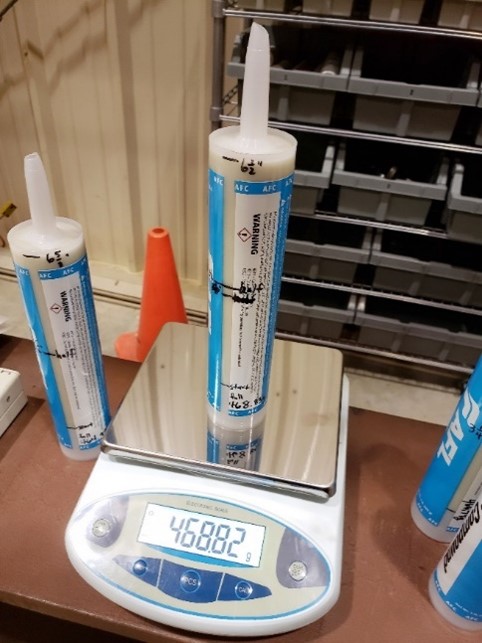

Evaluate the Effects of Joint Compound Application in Compression Connector Performance: Accelerated aging at 93°C of test lines assembled with different amounts of joint compound is to be continued into 2026 to evaluate the impact of joint compound on the thermal and electrical performance of two-stage compression connectors. In 2026, thermal-mechanical aging is anticipated to finish on the two-stage compression fittings with different amounts of joint compound applied, and post-accelerated aging evaluations are planned. An update to the Effects of Connector Compound Application in Overhead Transmission Compression Connector Performance report is anticipated.
Provide Training on Traditional Conductors: With the loss of experienced personnel, it is imperative that we educate and train new personnel efficiently and effectively. In 2026, EPRI intends on providing new training introducing different types of traditional conductors, their degradation mechanisms, inspection techniques, acceptance criteria, and mitigation methods.
Provide Tools and Resources on the Transmission Resource Center: The following calculators, tools, result summaries, and references are planned to be available on the Traditional Conductors and Connectors Transmission Resource Center:
| Resource Title | Resource Type |
|---|---|
| Overview of Causes of Compression Connector Failure | Reference |
| Visual Inspection | Reference |
| Dimensioning of Compression Connectors | Reference |
| Infrared Thermography of Compression Connectors | Reference |
| Radiography of Compression Connectors | Reference |
| Resistance Measurement of Connectors | Reference |
| Connectors 101 Training | Video Training |
Anticipated Deliverables
| Deliverable | Deliverable Type |
|---|---|
| Traditional Conductor and Connector Inspection Guide | Technical Update Report |
| Traditional Conductor and Connector Management Guide | Technical Update Report |
| Evaluation of Aged Traditional Conductors and Connectors | Technical Update Report |
| Effects of Connector Compound Application in Overhead Transmission Compression Connector Performance | Technical Update Report |
| Traditional Conductors 101 | Web-Based Training |
Past EPRI Work on Topic
| Product ID | Title | Description | Published Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3002030186 | Field Guide: Construction and Inspection of Compression Connectors for Overhead Transmission Lines | This guide describes typical applications, compression connector basics, construction methods, common assembly errors, and inspection methods. In addition, it provides a list of relevant technical and training resources. | 12/10/2024 |
| 3002030187 | Field Guide: Infrared Thermography for Overhead Transmission Lines—Insulators, Compression Connectors, Overhead Ground Wire, and Surge Arresters | This guide is designed to assist both skilled IR thermographers and experienced engineers in improving measurement accuracy. | 12/18/2024 |
| 3002030193 | Field Guide: Inspection of Conductors for Overhead Transmission Lines | This guide provides a general, field-deployable resource for utility professionals who are engagedin the inspection and assessment of overhead transmission lines. | 12/18/2023 |
| 3002029564 | Guidelines for Connector Inspection: Temperature Probe Evaluation and Member Survey Results | Various inspection techniques and methods for connectors are discussed and described including the benefits and challenges of each technique. This guide currently covers visual inspection, dimensioning, thermal measurements, infrared thermography, resistance measurements, and radiography of compression connectors. | 11/19/2024 |
| 3002029565 | Connector Management Guide: Degradation Modes of T-Connectors | This technical update provides how to create an inspection and management plan for compression connectors. | 11/19/2024 |
| 3002029566 | Evaluation of Aged Compression Connectors: Evaluation of a Failed T-tap Connector | This document provides anoverview of three different types of compression connectors, describes factors that contribute to compression connector failures, presents the EPRI process for evaluating field-aged connectors, and catalogs results from aged compression connector evaluations. | 11/11/2024 |
| 3002029567 | Effects of Connector Compound Application in Overhead Transmission Connector Performance | EPRI has set out to review, survey, and test connector compounds that have been in the market in the pastand that are currently being produced to better understand the impact of connector compounds on the performance of overhead transmission connectors,evaluate the compounds on the market, understand the degradation of connectors utilizing connector compounds, and how to apply connector compounds most effectively. | 12/17/2024 |