Collaborative Supplemental Projects EPRI participants can engage EPRI with supplemental projects. When a company funds EPRI annual research, 25% of the funds are set aside as self-directed funds (SDF). Utilities can use this to fund supplemental projects. Please contact your METT for more information on how supplemental project funds are allocated in your utility.
Implementation Opportunities
Supplemental projects can also be one-on-one efforts. Companies allocate their self-directed funds in different ways. Options for these projects can include:
- Field pilots of technologies
- Integration of research results
- Test specific equipment or scenarios
Examples related to current research could include:
- Full-scale structure testing, mechanical or electrical
- Comparative aging performance
Services and Capabilities
EPRI has many capabilities available to utilities as part of research work, supplemental projects, or service agreements. A selection of these include:
- Arc-flash testing
- Forensics and material analysis
- Mechanical and electrical testing of full-scale composite structures
Research Results Summaries
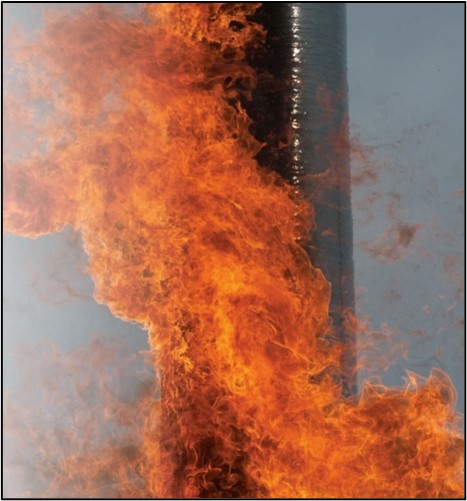

Evaluation of Wildfire Protection Methods for Composite Utility Structure Materials
Utilities in high wildfire threat areas are exploring technologies to reduce the susceptibility of power lines to being damaged by the fire, or alternatively, a risk of causing fires. Composite structures have inherent resistance to damage from wildfires as the material is self-extinguishing. Additional protection may be added via the use of fire protection sleeves placed around the lower portion of the poles, or via intumescent coatings. Testing was performed by EPRI to evaluate the comparative performances of these techniques.
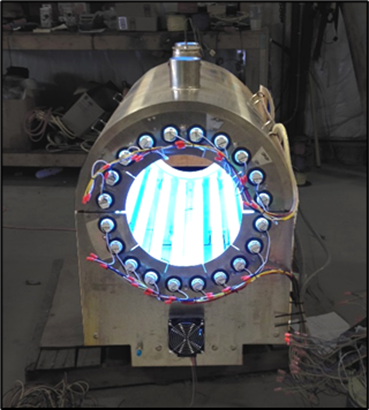
Effects of Environmental Aging on Composite Poles
Composite poles as well as crossarms are manufactured using polymers that degrade when exposed to environmental stresses. The objective of this research is to determine the differences between the mechanical performances as well as comparative degradation effects on the composite structures resulting from exposure to ultraviolet radiation, heat and humidity; thereby assisting utilities in their selection of suitable poles for their specific application.
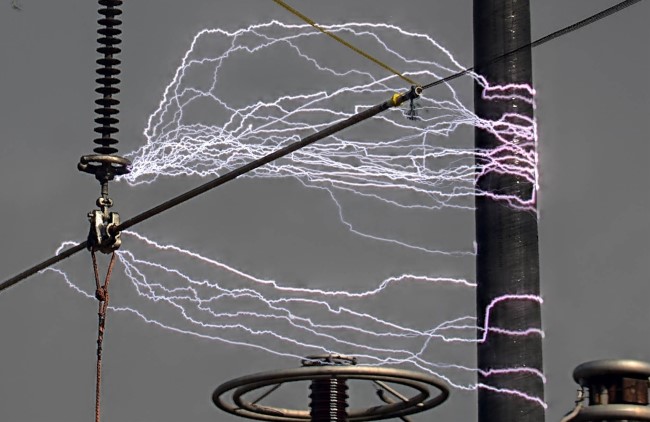
Recommendations for Grounding of Composite Utility Poles
Impulse testing was performed to determine optimum spacings for insulators when utilizing composite poles and crossarms. During testing, several grounding options and their effects on the composite structure were evaluated.
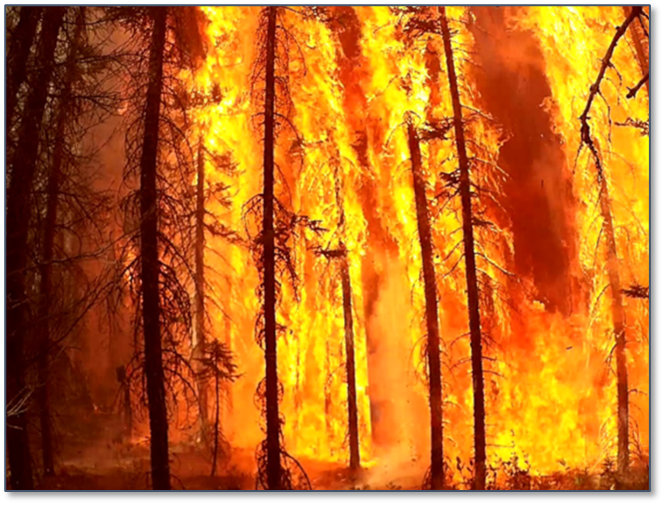

Effects of Wildfire Exposure on Small-Scale Composite Pole Samples
Utilities in high wildfire threat areas are exploring technologies to reduce the susceptibility of power lines to being damaged by the fire, or alternatively, a risk of causing fires. Testing was performed by EPRI to evaluate the comparative resistance to damage from wildfire conditions of composite pole samples from each manufacturer.
Reference Information
Videos
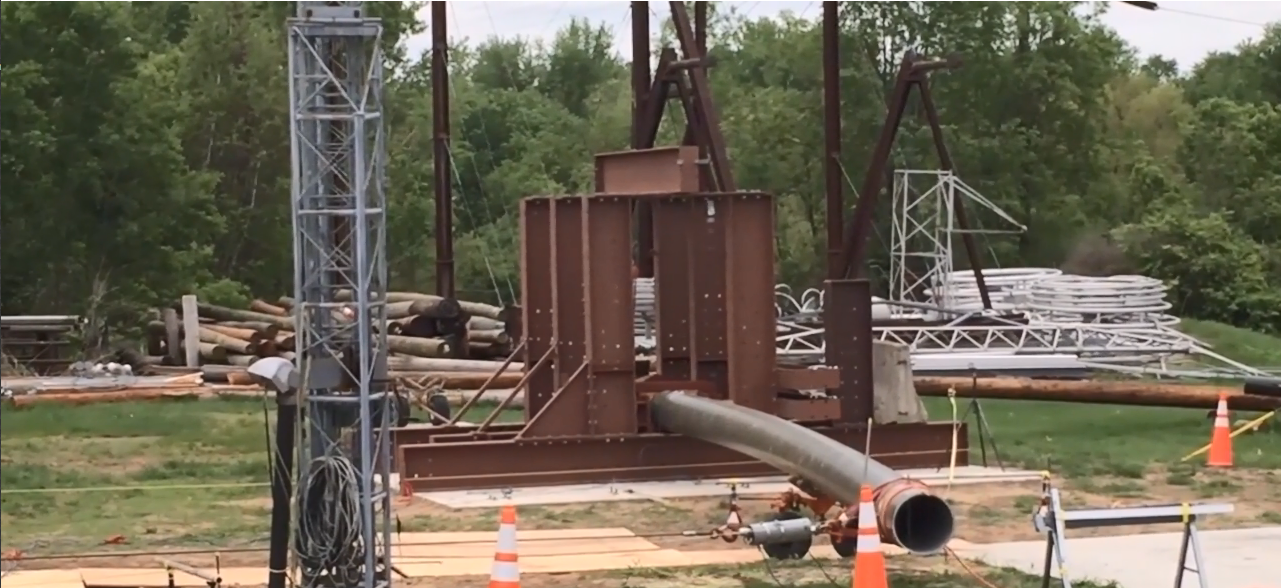

Loading composite utility poles to failure to understand failure modes
New and aged composite poles from each manufacturer were loaded to failure to compare how their mechanical properties change over time, and the types of failure characteristics experienced. It should be noted that poles from the various manufacturers were not selected based on equivalent performance. Video shows testing of poles in their new condition. Equivalent poles were subjected to accelerated aging for 3 years and then subjected to identical testing to identify any changes in ultimate load and deflection.