Calculators
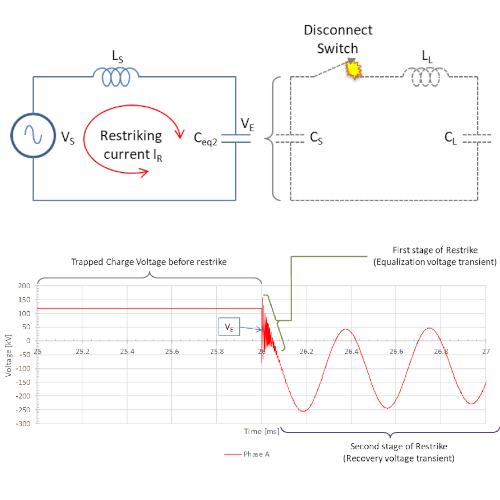
Whip Testing (Web-based) a simplified software calculator has been developed to calculate the test circuit component values for a range of input parameters. With the known test circuit parameters, this software tool can also calculate the expected TRV transients and oscillation frequencies, that can be compared to oscillographs captured during testing.
Research Results Summaries

ESRI Survey123 Inspection Form for Commissioning of New Line Switches
Procedures for the deployment of inspection forms for the commissioning of new overhead transmission line switches using ArcGIS Survey123.
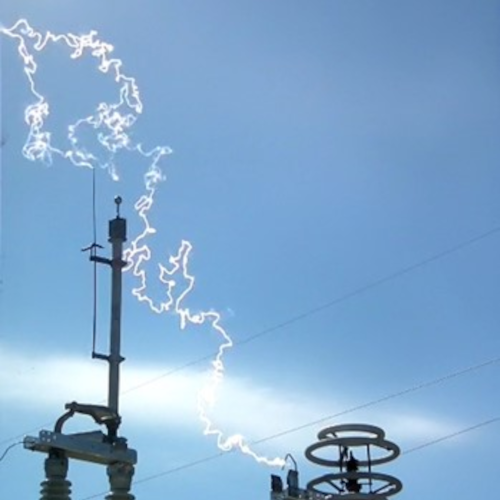

Quick Break Whip Testing – Intro on Interrupting Capacitive Currents
Information on quick break whip switches and why there is a need to test them can be obtained by clicking on the link.

Line Switch Commissioning 101
There are many reasons why line switches do not work correctly over time. Utilities can avoid many operational issues if the component is specified for actual environmental exposure conditions and installed per the design requirements.
Reference Information

Selected Standards
This page lists selected standards related to overhead line switches (disconnect switches) and associated components, organized by components and year of publication. Descriptions of most listed documents are taken from the respective websites.