Reference Information
Key information from reference documents and guides (e.g.) or succinct descriptions of concepts (e.g. what is risk and how do I visualize it)
This the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Key information from reference documents and guides (e.g.) or succinct descriptions of concepts (e.g. what is risk and how do I visualize it)
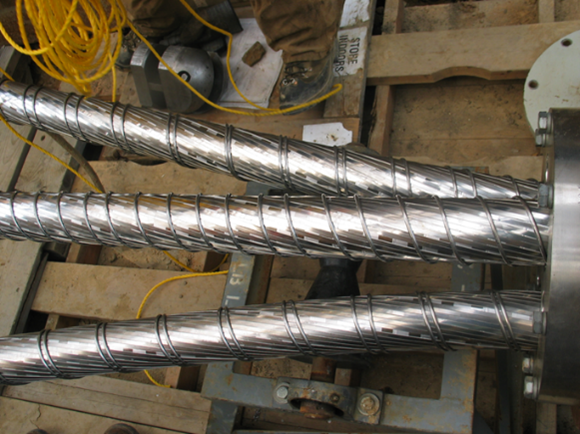




Mechanical Bending Rig Extruded-dielectric underground transmission cables experience thermo-mechanical bending during operation and daily load cycling. EPRI is conducting research into their effects on the cables to aid in design of suitable cable constraint and support systems. The study is achieved first through measurements of mechanical parameters of various cable constructions, finite element analysis of the installed conditions, and then empirical verification by a full-scale test rig comprised of a length of full-sized duct. The results of the mechanical parameter tests are incorporated into finite element analysis theoretical models to assist in extruded-dielectric cable installations and designs and enhance operation and maintenance of such cable systems.
Buried Steel Pipe Corrosion Test Station Corrosion management of transmission structures has become increasingly important. The EPRI Buried Steel Pipe Corrosion Test Station is designed to aid in condition monitoring of buried steel pipes for underground transmission pipe-type cable systems. The test station allows the utility to monitor pipe conditions at locations identified with high corrosion risks. These measurements can be used to gain a better understanding of cathodic protection levels, mass loss, corrosion rate, and stray currents on the pipe around the installed test station. The test station measurements are used to help guide corrective maintenance actions and decisions for the buried steel pipe system.
Dissolved Gas Analysis
Robotic Inspection for Underground Vaults
| Test Facility | Location |
|---|---|
| Cable Mechanical Bending | Charlotte |
| Buried Pipe Corrosion | Charlotte |
| Vault Component Corrosion | Charlotte |
| Full-scale Test for Paper Cable | Lenox |
| Sensor Research | Charlotte |
| Robotic Inspection | Charlotte |
| Cable Failure Root Cause | Charlotte |
Description of each test facility (coming soon)
Corrosion management of transmission structures has become increasingly important. The EPRI Buried Steel Pipe Corrosion Test Station is designed to aid in condition monitoring of buried steel pipes for underground transmission pipe-type cable systems. The test station allows the utility to monitor pipe conditions at locations identified with high corrosion risks. These measurements can be used to gain a better understanding of cathodic protection levels, mass loss, corrosion rate, and stray currents on the pipe around the installed test station. The test station measurements are used to help guide corrective maintenance actions and decisions for the buried steel pipe system.
The EPRI Buried Steel Pipe Corrosion Test Station is a flush mount terminal station with connections to buried bonded and floating steel coupons and the steel pipe. The test station includes a terminal board with switches, a shunt, and lead connections to measure relevant currents and potentials by a digital multimeter (DMM) or other measuring device. The terminal board allows for measurements of “On”, “Instant Off”, and de-polarized potentials of the pipe, as well as current flows between the bonded coupons and pipe. The current and potential measurements can be taken in a regular inspection cycle, or through installed data loggers for higher data sample intervals. Two additional exothermic weld connections are secured to the pipe to provide a secured mechanical and electrical bond to the terminal board.
The EPRI Buried Steel Pipe Corrosion Test Station includes the following functions:
The figures below show a 3-D model of the EPRI Buried Steel Pipe Corrosion Test Station installation (left) and the terminal board design for taking current and potential measurements (right).


Underground transmission cables experience thermo-mechanical bending during daily load cycles. EPRI investigates the impact of such thermo-mechanical forces and bending on design, operation, and long-term performance of underground transmission cables. One of the test setups used in this analysis is the EPRI transmission cable mechanical bending rig. The test rig is installed in the EPRI Laboratory in Charlotte, NC. Results from this test rig can be used in design, operation, and maintenance of such cable systems.
The purpose of the test rig is to perform accelerated aging tests on select cable samples through cyclical bending. The test rig comprises of a metal bed and a mock pipe wall with the cable sample constrained at both ends. The cable sample is clamped at the cable conductor on each end and tension and compression force is applied axially to one end of the conductor until a bend forms and the cable touches the mock pipe wall. The force is recorded at the mock pipe wall and once the user defined force is met, the actuator retracts, and the cable is pulled straight completing one cycle. The cable sample is restricted to a single plane to achieve repeatable, localized bending. The applied force is monitored using load cells situated at the driving actuator and the mock pipe wall. The test rig bends and straightens the cable sample for 30,000 cycles to simulate a service life of 40 years.
After the bending test is complete, the cable sample is analyzed layer-by-layer for signs of degradation or damage resultant from the cyclical motion. Visual inspection and material analysis are performed for each critical layer, such as, outer jacket, metallic shield/sheath, insulation, and conductor. The material analyses include factors that may affect the life expectancy of a cable.
The test rig includes a data acquisition system to measure and record test data during the testing and operation. Guide rails and cable restraints are adjusted to meet the cable testing requirements of different cable types and construction. The figures below show the EPRI transmission cable mechanical bending rig (left) and a side view of the installed extruded transmission cable sample (right).
In summary, functions of the mechanical bending test rig include:

