Project Overview
Objective
Considering the anticipated growing demand for transmission capacity, which is fueled by a combination of changing generation patterns and emerging electricity-intensive technologies, utilities will find value in producing higher performing overhead lines which feature increased performance in terms of capacity, transmission efficiency, and reliability.
The objectives of this project are closely aligned to the EPRI vision of producing safe, affordable, environmentally responsible, and reliable electricity. This mission is reflected in the transmission line design space where multiple aspects of system performance converge in the design process. The objectives of this project are to:
- Facilitate the engineering and construction of higher performing transmission lines
- Enhance the knowledge and skill of engineers performing line design
- Assist in the research and development of tools and solutions that complement the line engineering effort
Reseach Value
Research in overhead transmission line design provides guidance on proper selection, design, and application of line components and enrichment of transmission line engineers. Value provided in this project includes:
- Reduction of capital and operational expenditures by optimal selection of structural and geotechnical systems
- Increased safety through the proper specification of line components
- Increased performance and efficiencies of transmission line engineers through advanced training courses
- Improved electrical performance through analysis of high-voltage electrical effects.
Approach
In 2026, EPRI intends to perform the following tasks to meet the project objectives:

Update the EPRI AC Transmission Line Reference Book - 200 kV and Above (The Red Book): EPRI plans to commence an update of Chapter 13 - Considerations for Inspection and Maintainability. This update aims to enhance inspection and live line maintenance of advanced overhead transmission lines with new technologies, methodologies, and best practices. It includes improvements in materials, techniques, and structural design for safe and efficient inspection and maintenance.

Update the EPRI Transmission Line Reference Book: Conductor and Structure Motion (The Orange Book): Minor (editorial) updates are expected on The Orange Book in 2026, which will be released for the benefit of new members.

Update the EPRI Transmission Line Reference Book: 115–400 kV Compact Line Design (The Blue Book): Minor (editorial) updates are expected on The Blue Book in 2026, which will be released for the benefit of new members.

Add Cost Estimates to the Optimal Pole Material Selection Guide: This multi-year research effort is focused on helping engineers make the best decisions with regards to transmission pole material selection between wood, steel, concrete, fiber-reinforced polymer, and ductile iron. The guide contains a qualitative review of each material type, representative structural designs, and pertinent design recommendations. In 2026, EPRI will focus on producing cost estimates for each material type to include procurement and installation expenses.
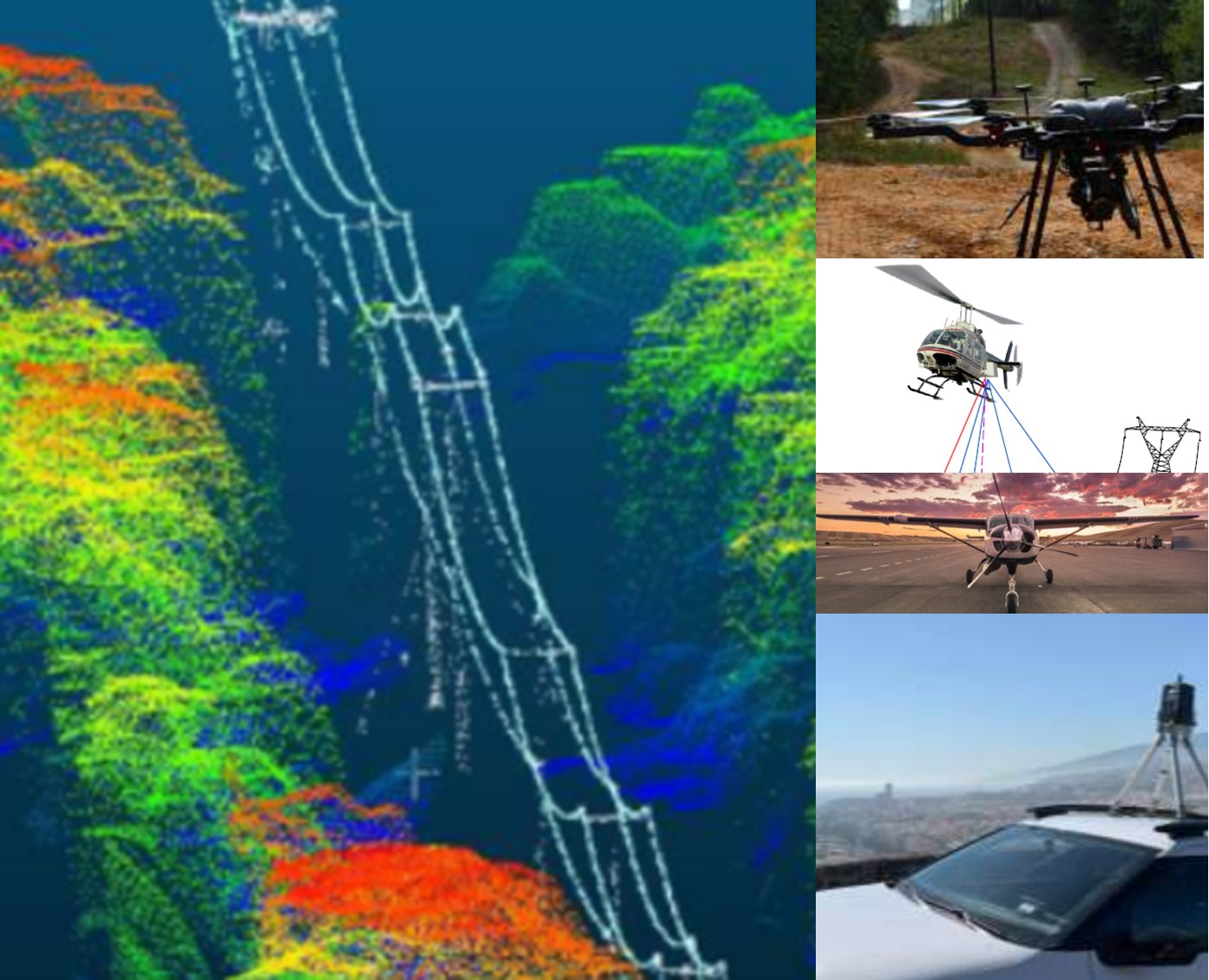

Develop Best Practices for LiDAR Data in Overhead Line Design Software: With the proliferation of a wide range of LiDAR-capturing methods (including traditional airborne, uncrewed aircraft system (UAS)-based, and land-based platforms) there is scope for improved specification development to ensure optimal integration with line design software for new construction, increased power flow, vegetation management, and structure evaluation applications. In addition, artificial intelligence (AI) methods show promise in automated point cloud classification as well as digital twin development. In 2026, EPRI intends to begin evaluations on these new and emerging techniques.

Develop Safe Design Tension Limits of ACSS Conductor: Determining a safe conductor tension is a multi-faceted problem that requires understanding of the self-damping performance and fretting fatigue endurance of a conductor. This new initiative, which is a collaborative effort with project 35.015, aims to help solve this problem for aluminum conductor steel-supported (ACSS) conductor, as its self-damping and fatigue properties vary significantly from aluminum conductor steel-reinforced (ACSR) conductor. In 2026, EPRI intends to continue empirical testing on conductors to define tension limits.

Provide Orange Book Overview & Single Conductor Aeolian Vibration Training: EPRI aims to continue the production of selected training modules covering key chapters in The Orange Book. These events will be held in conjunction with EPRIU4T.
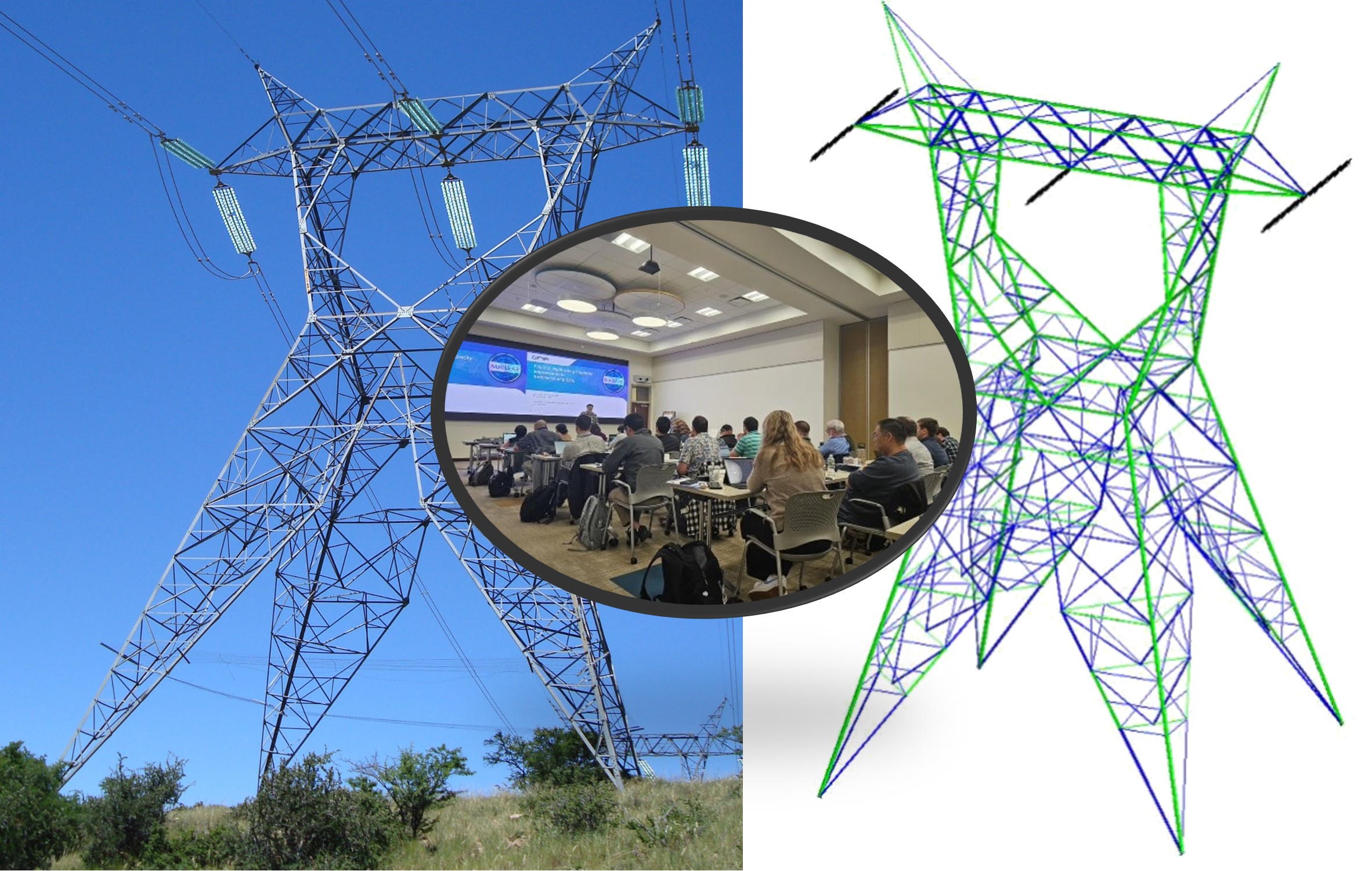

Provide Training Workshop on Lattice Tower Design: The advent of renewed 765-kV expansion has placed emphasis on steel lattice tower design, which is a support option facing skill depletion as more utilities adopt steel poles as a preferred support solution. EPRI aims to enhance skill in lattice tower design by hosting a workshop which covers essential elements of lattice tower design and effective modelling and optimization of lattice towers.
Produce a NESC Clearances Calculator: EPRI aims to produce an advanced calculator to automate the calculation of National Electric Safety Code (NESC) transmission line clearances as defined by NESC Rules 231–239. This versatile tool will accommodate a wide range of clearance scenarios and voltage levels, including both baseline tabulated clearances and alternative clearance calculations. The 2026 version of the calculator will be available in an Excel-based format, tailored for the 2023 NESC. It will serve as a valuable training tool and informational resource for transmission engineers.
Update the Optimal Line Tension Calculator (Op10): Op10 software is designed to determine the most cost-effective installed conductor tension, based on specific project variables, and to quickly determine the impact of a selected (or existing) conductor tension. Op10 will be updated to include new features as requested by users.
Update the Transmission Line Workstation Gen 2: Design and Vibration Module: This EPRI software tool was developed to facilitate engineers in evaluating different design options effectively. Algorithms in some of the design programs may require updating based on EPRI research. Updating of this software may also be required to improve user features, add new functionalities, or to be compatible with other industry software used by the design engineers.
Provide Tools and Resources on the Transmission Resource Center: The following calculators, tools, result summaries, and references are planned to be available on the Line Design Transmission Resource Center:
| Resource Title | Resource Type |
|---|---|
| EMFast Web | Calculator |
| EPRI AC Transmission Line Reference Book - 200 kV and Above (The Red Book) | Reference |
| EPRI Red Book Application Suite (Partial) | Calculators |
| EPRI Transmission Line Reference Book: Conductor and Structure Motion (The OrangeBook) | Reference |
| EPRI Transmission Line Reference Book: 115– 400 kV Compact Line Design (The BlueBook) | Reference |
| Leveraging Existing Infrastructure | Result Summary |
| Reconductoring, Tensioning, and Advanced Conductor Technologies for Increasing Capacity of Transmission Lines | Result Summary |
| Increasing Transmission Line Capacity Through Ratings | Results Summary |
| Optimal LineTension Calculator (Op10) Demonstration | Demonstration Video |
| Post Insulator Capacity Calculator (PICC) Demonstration | Demonstration Video |
| Vibratory Caisson Foundation Pull Test | Demonstration Video |